Removing tumors and growths within and around the facial region
Members of the dental profession, in particularly Dr. Clark, Dr. Cole, and Dr. Patel, and your dentist, are the most experienced and knowledgeable about the diseases that affect the oral cavity and the tissues surrounding it. While lesions within or around the oral cavity are usually benign, unfortunately, malignant lesions can develop within the mouth. However, if detected early, cancerous lesions can often be completely removed with minimal surgery.
 Regular hygiene appointments and routine follow up with your dentist is the best way to detect oral cancer early. If your dentist finds a suspicious lesion, you will be referred to our office to evaluate the area. After reviewing your medical history and checking the area in question, Dr. Clark, Dr. Cole, or Dr. Patel will decide if a biopsy is necessary. Small lesions can often be removed in entirety; larger lesions may require that Dr. Clark, Dr. Cole, or Dr. Patel excise only a representative sample of the area for diagnosis. The tissue will be sent to an oral pathologist, a doctor who specializes in identifying lesions within the mouth. Once the lesion has been identified, Dr. Clark, Dr. Cole, or Dr. Patel will discuss with you the diagnosis. Often a biopsy is the only surgical treatment necessary. However, if further treatment is required, Dr. Clark, Dr. Cole, or Dr. Patel will advise you of your options. Biopsies can be preformed with either local anesthesia or IV sedation.
Regular hygiene appointments and routine follow up with your dentist is the best way to detect oral cancer early. If your dentist finds a suspicious lesion, you will be referred to our office to evaluate the area. After reviewing your medical history and checking the area in question, Dr. Clark, Dr. Cole, or Dr. Patel will decide if a biopsy is necessary. Small lesions can often be removed in entirety; larger lesions may require that Dr. Clark, Dr. Cole, or Dr. Patel excise only a representative sample of the area for diagnosis. The tissue will be sent to an oral pathologist, a doctor who specializes in identifying lesions within the mouth. Once the lesion has been identified, Dr. Clark, Dr. Cole, or Dr. Patel will discuss with you the diagnosis. Often a biopsy is the only surgical treatment necessary. However, if further treatment is required, Dr. Clark, Dr. Cole, or Dr. Patel will advise you of your options. Biopsies can be preformed with either local anesthesia or IV sedation.
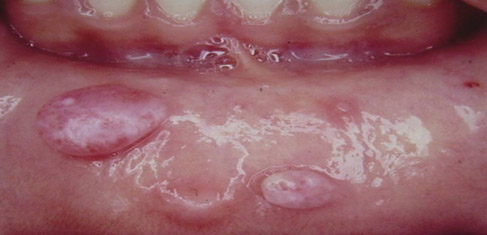
 The most common oral lesions are nodules or bumps on the soft tissue adjacent to your teeth. These lesions are usually benign and either represents scar tissue or an obstructed salivary gland. The soft tissue lesions that are most concerning are ulcers that fail to heal within two weeks, white lesions, red lesions, dark blue lesions, and lesions that bleed easily. These lesions need to be biopsied to make sure they are not malignant.
The most common oral lesions are nodules or bumps on the soft tissue adjacent to your teeth. These lesions are usually benign and either represents scar tissue or an obstructed salivary gland. The soft tissue lesions that are most concerning are ulcers that fail to heal within two weeks, white lesions, red lesions, dark blue lesions, and lesions that bleed easily. These lesions need to be biopsied to make sure they are not malignant.
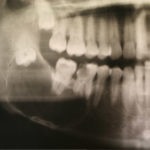
Lesions that appear on x-rays around the roots of teeth, or the crowns of impacted teeth are often benign cysts. Usually removing the cyst, or both the cyst and the adjacent tooth is the only treatment that is necessary. Occasionally more aggressive cysts will require removal of the surrounding bone.
Fortunately, it is rare that lesions develop within or around the oral cavity. Most lesions are benign and require minimal surgery to remove them. Early detection is very important. The best way to detect an abnormally within your mouth is to see your dentist once or twice a year for examination, or to call our office for consultation regarding any suspicious areas.